Page 11 - 北京京煤集团总医院第十一届·2023学术年会论文集
P. 11
北京京煤集团总医院 第十一届·2023 学术年会论文集
Figure 5: Nomogram model. (A) SMARCC1, SETD2, KMT2B, and CHD8 were used to construct a
nomogram model to predict the prognosis of patients with severe asthma. (B) Receiver operating
characteristic curve to determine the performance of the nomogram model. (C) Calibration curve.
3.4 Potential drugs for treating severe asthma
DSigDB was used to predict drugs for the treatment of severe asthma, and the results showed
that the ten most effective drugs would be lanatoside C, cefepime, methapyrilene, sulpiride, vitamin
E, ouabain, metoclopramide, pramocaine, dirithromycin, and tamibarotene.
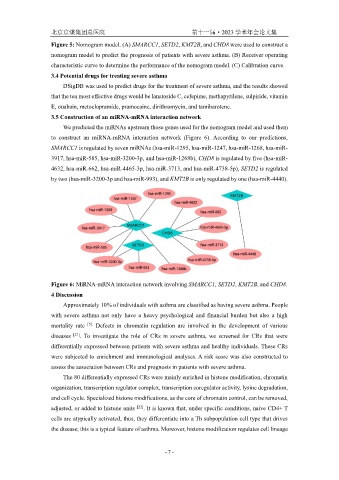
3.5 Construction of an miRNA-mRNA interaction network
We predicted the miRNAs upstream those genes used for the nomogram model and used them
to construct an miRNA-mRNA interaction network (Figure 6). According to our predictions,
SMARCC1 is regulated by seven miRNAs (hsa-miR-1295, hsa-miR-1247, hsa-miR-1268, hsa-miR-
3917, hsa-miR-585, hsa-miR-3200-3p, and hsa-miR-1268b), CHD8 is regulated by five (hsa-miR-
4632, hsa-miR-662, hsa-miR-4465-3p, hsa-miR-3713, and hsa-miR-4738-5p), SETD2 is regulated
by two (hsa-miR-3200-3p and hsa-miR-993), and KMT2B is only regulated by one (hsa-miR-4440).
Figure 6: MiRNA-mRNA interaction network involving SMARCC1, SETD2, KMT2B, and CHD8.
4 Discussion
Approximately 10% of individuals with asthma are classified as having severe asthma. People
with severe asthma not only have a heavy psychological and financial burden but also a high
mortality rate [5]. Defects in chromatin regulation are involved in the development of various
diseases [21] . To investigate the role of CRs in severe asthma, we screened for CRs that were
differentially expressed between patients with severe asthma and healthy individuals. These CRs
were subjected to enrichment and immunological analyses. A risk score was also constructed to
assess the association between CRs and prognosis in patients with severe asthma.
The 80 differentially expressed CRs were mainly enriched in histone modification, chromatin
organization, transcription regulator complex, transcription coregulator activity, lysine degradation,
and cell cycle. Specialized histone modifications, as the core of chromatin control, can be removed,
adjusted, or added to histone units [22] . It is known that, under specific conditions, naive CD4+ T
cells are atypically activated, thus, they differentiate into a Th subpopulation cell type that drives
the disease; this is a typical feature of asthma. Moreover, histone modification regulates cell lineage
- 7 -