Page 74 - 北京京煤集团总医院第十一届·2023学术年会论文集
P. 74
北京京煤集团总医院 第十一届·2023 学术年会论文集
Table 3 Multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Study Heterogeneity
Risk Factors RR 95% CI P
Number I² (%) P
Patient related factors
Male sex 4 0.0 0.584 1.41(0.76-2.05) 0.001
Hypertension 7 0.0 0.596 1.47(1.18-1.77) 0.001
Diabetes 3 31.3 0.233 1.17(0.29-2.06) 0.010
Anticoagulation 2 0.0 0.450 3.56(0.66-6.46) 0.016
Aspirin 3 60.0 0.082 1.46(0.98-1.93) 0.001
Polyp-related factors
polyp number ≥3 2 42.2 0.188 2.35(0.88-3.82) 0.002
Polyp size 4 69.6 0.020 1.17(1.13-1.22) 0.001
≥10 mm 5 0.0 0.540 2.13(1.42-2.83) 0.001
Polyp size
>10 mm 2 30.1 0.231 3.65(2.17-5.14) 0.001
Pedunculated polyp 4 58.4 0.066 1.73(0.33-3.12) 0.015
Right semicolon 5 0.0 0.797 2.23(1.38-3.08) 0.001
Operational related factors
Resection EMR 4 0.0 0.084 1.69(-0.01-3.38) 0.051
method HSP 2 0.0 0.786 1.63(-0.00-3.27) 0.050
EMR: endoscopic mucosal resection; HSP: hot snare polypectomy.
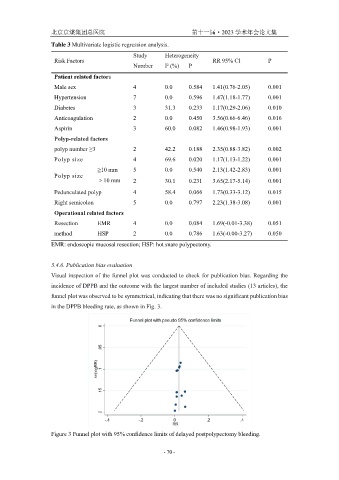
3.4.6. Publication bias evaluation
Visual inspection of the funnel plot was conducted to check for publication bias. Regarding the
incidence of DPPB and the outcome with the largest number of included studies (13 articles), the
funnel plot was observed to be symmetrical, indicating that there was no significant publication bias
in the DPPB bleeding rate, as shown in Fig. 3.
Figure 3 Funnel plot with 95% confidence limits of delayed postpolypectomy bleeding.
- 70 -